Vol 19 No 1 (2024)
Editorial
-
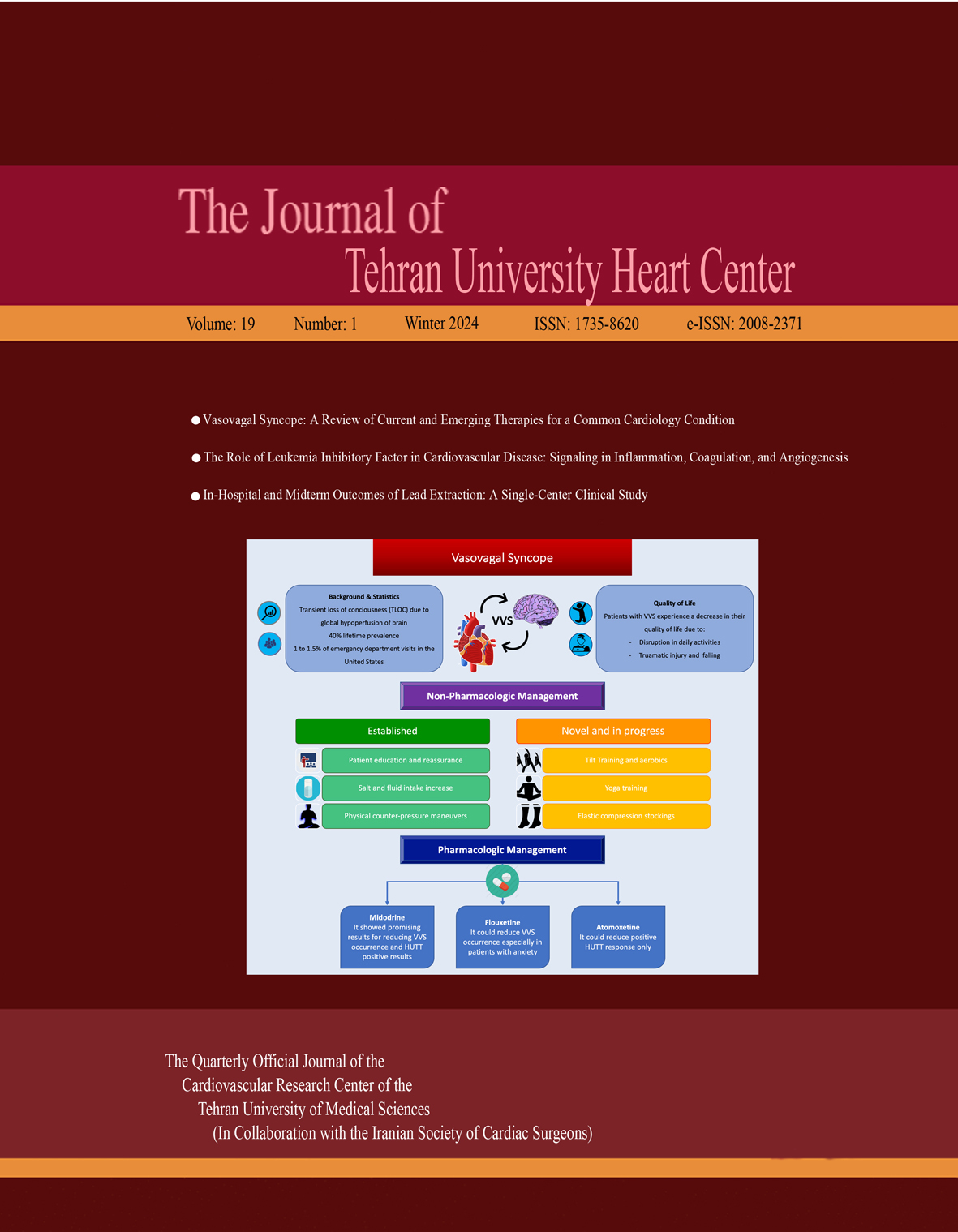
Vasovagal syncope (VVS), characterized by transient loss of consciousness, is among the most prevalent reasons for emergency visits worldwide. Although benign in nature, VVS can be accompanied by traumatic injury, leading to morbidity and decreased quality of life, especially in those with VVS recurrence. The management includes non-pharmacologic and pharmacologic therapies (if resistant), patient education and reassurance, salt and fluid intake increase, and physical counter-pressure maneuvers. Among medications, midodrine has shown promising results in reducing VVS recurrence and positive head-up tilt tests. Fluoxetine and atomoxetine also might be suitable candidates for VVS therapy. Permanent pacemakers, such as closed-loop stimulation, are under research and can be effective in cases unresponsive to medical treatment. In summary, while data are scarce regarding the definite treatment of VVS, there is a need for further research with novel, easy-to-use and cost-effective therapeutic methods to enhance quality of life and prevent traumatic injury.
Review Article(s)
-
Background: Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is one of the principal causes of mortality in the world. Various factors have been identified in the pathogenesis of CVD. Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) as a secretory cytokine is one of these factors. The LIF receptor is located on endothelial cells and plays a role in the expression of specific genes in these cells. Endothelial cells are the innermost cells of blood vessels, and defects in these cells cause endothelial dysfunction and eventually CVD.
Methods: The present study is based on PubMed database information (1982–2022) using the following words: “cardiovascular disease,” “endothelial cells,” “leukemia inhibitory factor,” and “angiogenesis.”
Results: LIF can cause arteriosclerotic plaques by activating inflammatory mechanisms in monocytes through the induction of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression. LIF can also induce vascular endothelial growth factor expression by activating signaling pathways, eventually leading to angiogenesis. Additionally, it can activate the coagulation cascade by factor VII production promotion within endothelial cells.
Conclusion Understanding the interplay between LIF and the inflammation pathways, coagulation, and angiogenesis as key factors in CVD occurrence raises the possibility of targeting this factor as a potential strategy to mitigate CVD risk.
Original Article(s)
-
Background: Lipid metabolism disorders are among the most common metabolic diseases that are increasing globally and are associated with chronic metabolic disturbances. The present study aimed to determine the knowledge and practice of internal medicine physicians concerning lipid disorders according to the AHA, AACE, ESC-EAS, and NCEP-ATP-III guidelines.
Methods: This descriptive-analytical cross-sectional study selected a convenience sample of 220 internal medicine specialists from January through September 2021 in Tehran and some other Iranian cities. A 25-item researcher-designed questionnaire was used. Suggested scenarios were designed by emphasizing the points of difference in the guidelines. Content validity was approved by 10 tenured faculty members, and reliability was tested with the test-retest method.
Results: Women comprised 60% of the population. In addition, 3.2% (n=7) of the physicians had poor knowledge, 95.0% (n=209) had moderate knowledge, and 1.8% (n=4) had good knowledge of lipid disorders based on international guidelines. Moreover, performance regarding lipid disorders was poor in 25 (11.4%), moderate in 164 (74.5%), and good in 31 (14.1%) physicians. The knowledge score decreased, whereas the practice score increased with age. The knowledge score of female physicians was significantly higher than that of their male counterparts. The knowledge score was negatively correlated with the physician’s years of experience.
Conclusion: The knowledge and performance of internists regarding dyslipidemia were rated moderate according to the AHA, AACE, ESC-EAS and NCEP-ATP III guidelines. -
Background: The rate of lead extraction has steadily increased alongside the extensive use of cardiovascular implantable electronic devices. Data on the complications and safety of this challenging procedure are limited. We investigated in-hospital and midterm outcomes following lead extraction.
Methods: Data were retrieved from 51 patients who underwent pacemaker/defibrillator lead extraction procedures at Tehran Heart Center between 2016 and 2021. The procedural success rate, patients’ demographic characteristics, and in-hospital and midterm procedure-related complications were investigated.
Results: Fifty-one patients were enrolled, including 44 men (86.3%). A total of 109 leads were extracted, with a 90.2% complete procedural success rate. In-hospital death occurred in 4 patients (7.8%): 1 patient (1.9%) died from pneumonia, 1 (1.9%) from septic shock, and 2 (3.9%) from septic shock besides heparin‐induced thrombocytopenia. Adverse events in 3 patients (5.8%) were directly related to the procedure: 1 patient (1.9%) suffered lung laceration and hemorrhage, 1 (1.9%) sustained subclavian injury, and 1 (1.9%) developed tamponade. Neither reinfection nor rehospitalization was observed during follow-up.
Conclusion: Lead extraction can be considered a highly successful procedure with a low rate of death-related events and complications. -
Background: Myocardial infarction is one of the leading causes of death in the world and accounts for 23% of mortalities. Self-care for senior patients with myocardial infarction can reduce complications, multiple hospitalizations, and financial costs.
Methods: This clinical trial was performed on 128 older adults with myocardial infarction. Available sampling was done via block random sampling among patients at the Heart Clinic of Booali Hospital, Qazvin, Iran. Data were collected through interviews and demographic and self-care questionnaires regarding heart disease. Data analysis was conducted using R software, version 4.1.0, and via the mixed-effects model method and post hoc and contrast tests.
Results: The mean age of the study population was 65.54±4.50 years. Before the intervention, self-care maintenance was not significantly different between the 2 groups. After the intervention, a statistically significant difference was observed between the groups (P=0.001). No statistically meaningful difference concerning self-care monitoring existed between the 2 groups at the beginning of the study (P=0.03); however, a significant difference emerged after the intervention (P=0.001). A difference existed between the groups regarding self-care confidence study commencement in that the self-care confidence level in the control group was higher (P=0.013), but no difference was observed following the intervention. Nonetheless, after 1 month, the groups were significantly statistically different (P=0.003) in that the self-care confidence level in the intervention group increased.
Conclusion: Mobile health could improve self-care in older adults with myocardial infarction. -
Background: Obesity is considered a widespread concern internationally. Few studies have investigated the relationships between dairy consumption and hypertension and obesity. Therefore, this study examined the above concern in students.
Method: This cross-sectional study was conducted on 292 male students (18–30 y) living in the dormitories of Tabriz University of Medical Sciences. Students were selected via the multistage stratified random sampling method. Demographic information, anthropometric measurements, blood pressure (BP) readings, and a semi-quantitative validated questionnaire assessing dairy consumption (including a 24-hour dietary record covering 2 typical days and a holiday) were collected. After all the questionnaires were reviewed, they were coded and analyzed with Nutritionist IV software.
Results: The average age of the subjects was 22.36 years. The mean±SD values of body mass index (BMI), waist circumference, waist-to-hip ratio, and waist circumference-to-standing height ratio were 22.68±2.58 kg/m², 80.95±7.81 cm, 0.85±0.04, and 0.46±0.04 among the studied population, respectively. The mean±SD values of systolic and diastolic blood pressure were 111.84±10 mm Hg and 70.99±8 mm Hg, respectively. Milk consumption was associated with a low waist circumference (95% credible interval, 1.005 to 4.580; P=0.046). The odds of hypertension (defined as BP>120/90 mm Hg) were 2.686 times higher in the overweight and obese group than in the normal BMI group. The risk of hypertension was 1.045 times higher for individuals with abdominal obesity than for those who did not consume dairy products.
Conclusion: Milk consumption was associated with a low waist circumference. The correlations between systolic blood pressure and anthropometric factors were statistically significant. BMI, waist circumference, and waist-to-hip ratio were positively associated with systolic blood pressure. -
Background: Acute heart failure is a common clinical syndrome leading to hospital admission, with few evidence-based therapies for managing congestion. This trial aims to assess the efficacy of acetazolamide combined with loop diuretics in achieving decongestion among patients who fail to respond to oral diuretics and progress to acute decompensated heart failure in the absence of injectable furosemide.
Methods: This single-center, double-blind randomized controlled trial with a 1:1 allocation ratio aims to evaluate 130 patients admitted to the infusion ward. Participants will receive standard furosemide treatment and be randomized to either oral acetazolamide (250 mg twice daily) or placebo for 3 consecutive days. The primary objective is to assess the efficacy of combined oral acetazolamide and furosemide therapy in achieving decongestion. The prespecified secondary outcomes include the following: N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide levels on day 30, readmission rates within 3 months, health-related quality of life as assessed by the Heart Failure Quality of Life Questionnaire at 3 months, and changes in weight, creatinine levels, urinary sodium excretion, potassium levels, and hematological indices from the complete blood count on day 3 of the trial.
Conclusion: Diuretic resistance commonly occurs in patients with heart failure, underscoring the urgent need for innovative interventions that can effectively address the limitations of current diuretics, including diuretic resistance and electrolyte imbalances, while enhancing their efficacy in this patient population. -
Background: Fractional flow reserve (FFR) is crucial to evaluating coronary artery stenosis in patients diagnosed with chronic coronary syndrome (CCS). By assessing the severity of stenosis, FFR assists in determining whether percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is necessary.
Methods: Conducted at Tehran Heart Center from 2013 through 2017, this cohort study involved 52,248 CCS patients who underwent coronary angiography. Among them, 598 symptomatic individuals, despite receiving comprehensive medical treatment, underwent FFR assessment. Subsequently, 225 patients with positive FFR (≤0.80) underwent PCI, while 373 patients received solely medical treatment. The patients were monitored for 3 years to evaluate primary and secondary endpoints.
Results: After 3 years, the PCI group demonstrated a lower incidence of the primary composite endpoint, consisting of all-cause mortality, nonfatal myocardial infarction, repeat target vessel/lesion revascularization (TVR/TLR), and coronary artery bypass graft surgery, than the medical treatment group (HR, 0.85; 95% CI, 0.74 to 0.98; P=0.012). Additionally, urgent TVR/TLR significantly decreased in the PCI group (HR, 0.56; 95% CI, 0.42 to 0.74; P<0.001).
Conclusion: FFR-guided PCI demonstrated effectiveness in reducing long-term major adverse cardiac events, primarily by lowering the incidence of TVR/TLR. The results emphasize the significance of FFR-guided PCI in addressing stenosis rather than alleviating ischemia.
Case Report(s)
-
Absent pulmonary valve syndrome (APVS) is a rare congenital anomaly characterized by rudimentary PV tissue with variable degrees of PV stenosis and regurgitant pulmonary blood flow. In most cases, it is associated with tetralogy of Fallot. In a minority of APVS cases, with an unknown frequency, intact ventricular septum (IVS), patent ductus arteriosus, and possible tricuspid atresia are present. This condition is known as non-Fallot type APVS.
We describe a case of an antenatal diagnosis of APVS with IVS, a large patent ductus arteriosus, and ascending aorta dilatation. The mother was referred to our center at 32 weeks of gestation due to cardiomegaly on sonography. Fetal echocardiography revealed cardiomegaly, right atrial and ventricular enlargement, aneurysmal dilatation of the main pulmonary artery, and mild dilatation of the pulmonary artery branches. Also observed were IVS, rudimentary PV tissue with severe to-and-fro turbulence across the PV, a widely open ductus arteriosus, ascending aorta dilatation, and levorotation of the heart.
After childbirth, our diagnosis was confirmed by echocardiography and surgery. The baby experienced severe respiratory distress. At 15 days of life, surgical intervention in the form of pulmonary artery arterioplasty was performed, resulting in good outcomes. The patient underwent follow-up for 6 months and showed reasonable health. -
Cancer is the second leading cause of death worldwide, and pericardial effusion is relatively common in these patients. What constitutes the best therapeutic method for treating pericardial effusion in patients with cancer is controversial. Recent decades have witnessed the introduction of percutaneous balloon pericardiotomy, an effective and less-invasive method with lower recurrence rates than pericardiocentesis for draining pericardial effusion in patients with cancer who have a poor prognosis.
We herein describe 2 patients with a history of metastatic melanoma and metastatic breast cancer, presenting with symptomatic massive pericardial effusions. The patients had experienced 2 episodes of cardiac tamponade in the preceding 4 to 5 months, treated via surgical drainage. In their current episode, they were both successfully treated via percutaneous balloon pericardiotomy, and there was no recurrence of significant pericardial effusion reported during the follow-up. -
Balloon aortic valvuloplasty (BAV) is a therapeutic option as palliative or bridging therapy in severe aortic stenosis, even though it is a risky procedure, especially in patients with concomitant left ventricular dysfunction. The use of percutaneous ventricular assist devices, such as the Impella CP, in this scenario provides optimal circulatory support and considerably reduces the risk of the procedure. Two patients with severe aortic stenosis and left ventricular dysfunction underwent BAV with the support of the Impella-CP. The Impella CP provided adequate support in both high-risk patients and safely allowed BAV.
Letter to the Editor
-
No Abstract No Abstract No Abstract