Vol 15 No 1 (2020)
Original Article(s)
-
Background: The optimal surgical plan to correct the simple transposition of the great arteries (TGA) is the arterial switch operation (ASO). This study aimed to assess the outcomes of ASO in infants with simple TGA with a special focus on the time of surgery.
Methods: This retrospective study enrolled 105 infants with simple TGA who underwent ASO and categorized them into 3 groups based on the time of repair: first week of life: Group A; second week of life: Group B; and third week of life: Group C. The endpoints, comprised of an assessment of pre- and postoperative outcomes, complications, and survival, were compared between the groups.
Results: The mean age of the infants was 10.50±6.26 days, and 61 (58.1%) cases were male. The mean number of days on dopamine was 1.85±0.12 in Group A, 2.48±0.03 in Group B, and 2.67±0.08 in Group C (P<0.001). The mean number of days on epinephrine was 1.25±0.07 in Group B and 1.27±0.08 in Group C (P<0.001). The mean number of days on the ventilator was 3.52±0.20 in Group A, 4.56±0.24 in Group B, and 5.06±0.21 in Group C (P<0.001). The mean number of days of ICU stay was 6.69±0.21 in Group A, 8.46±0.57 in Group B, and 9.70±0.64 in Group C (P<0.001). The infants in Group A had a greater survival rate (97.0%) than those in Group B (94.1%) and Group C (78.4%) (P=0.042).
Conclusion: ASO in infants with simple TGA can be done within the first week of life with satisfactory outcomes and survival. -
Background: Self-efficacy in self-care behaviors is an effective framework for measuring patients’ degree of ability to perform self-care behaviors that significantly affect their recovery process and quality of life. This study was designed to investigate the effects of education based on self-efficacy strategies on self-care behaviors in heart failure patients.
Methods: A semi-experimental study was conducted on 80 heart failure patients divided into 2 equal groups of test and control. The intervention group received three 60-minute practical and theoretical training sessions based on self-care and self-efficacy strategies, while the control group received the usual care services. Self-care behaviors and self-efficacy were evaluated before training, shortly after training, and 3 months after the training program using the Sullivan self-efficacy questionnaire for heart failure patients and the European self-care behaviors questionnaires.
Results: The mean age of the patients was 55.00±8.48 and 51.61±8.51 years in the intervention and control groups, respectively. Women comprised 73.7% (n=59) of the study population. The mean score for the self-care and self-efficacy questionnaires in the experimental group was 23.50±6.58 and 18.57±6.64, correspondingly, before the intervention, which increased to 42.64±6.74 (P<0.014) and 32.29±7.06 (P<0.001), respectively, shortly after the intervention. A significant improvement also occurred at 3 months’ follow-up (P<0.001). Self-care behaviors also revealed a positive correlation with self-efficacy shortly after the intervention (r=0.82, P<0.001) and 3 months after the intervention (r=0.85, P<0.001).
Conclusion: The implementation of educational interventions based on self-efficacy strategies could have positive effects on health-promoting behaviors among heart failure patients. -
Background: Heart transplantation is a major procedure which imposes high emotional stress on patients. Illness perception (IP) is a psychological issue which affects psychological adjustment after transplantation. This study aimed to investigate the association between IP and emotional status in Iranian post-heart transplantation patients.
Methods: The present cross-sectional study, conducted between 2018 and 2019 in Imam Khomeini Hospital, Tehran, Iran, recruited 121 post-heart transplantation patients. IP was measured using the Brief Illness Perception Questionnaire (B-IPQ), and emotional status was measured using the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale. The association between IP and depression/anxiety was assessed.
Results: Men comprised 80.2% of the study population. The mean age of the participants was 43.9±12.95 years. Definite caseness for depression and anxiety was reported in 11.6% and 18.2% of the participants, respectively. The median score of IP was 55. The association between anxiety and IP in total IP and the 3 dimensions of IP was statically significant (P=0.015, P=0.018, P=0.002, and P=0.023 for the cognition, emotion, and understanding dimensions and the total IPQ, respectively). Additionally, the association between depression and IP was significant (P=0.001, P=0.029, and P=0.002 for the cognition and emotion dimensions and the total IPQ, correspondingly, except for the understanding dimension). Furthermore, lower levels of anxiety in the patients showed a greater impact on IP than did depression.
Conclusion: There was a significant association between IP and depression and anxiety in our study population. Therefore, the diagnosis and management of anxiety and depression in heart transplantation patients may improve IP. The cross-sectional design of the present study precluded an investigation of the causality between IP and emotional status. -
Background: Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA) is a rare multi-systemic vasculitis, with cardiac involvement being one of its most serious manifestations. We aimed to systematically review and analyze the limited case reports of EGPA with cardiac involvement.
Methods: Based on the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines, we performed a systematic literature search for the case reports of EGPA with cardiac involvement in the MEDLINE database from 2011 until 2018. For each case, clinical data including sex, age, clinical presentation, electrocardiographic and cardiac imaging findings, the type of cardiac involvement, the available laboratory data (cardiac biomarkers, white blood cell count, eosinophilic count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, and antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody positivity), therapeutic regimen, and the outcome of the patients were collected and analyzed.
Results: A total number of 62 cases were included. The mean age was 48.29±15.60 years, and 51.6% were male. All the cases were in the active disease state. Cardiac symptoms, electrocardiographic abnormalities, abnormal biomarkers, and abnormal echocardiography were detected in 82.3%, 68.5%, 77.4%, and 96.8%, respectively. Cardiac magnetic resonance was done in 46.8% of the patients, and it was abnormal in all. The most common abnormal findings in echocardiography were systolic left ventricular dysfunction (83.9%) and pericardial effusion (37.1%). The most common type of clinical presentation was clinical heart failure (51.6%). Only 6.5% of the patients presented with tamponade. The overall prognosis was good.
Conclusion: Any part of the heart could be involved by EGPA. The results emphasize the necessity of in-depth cardiac evaluation in these patients.
Case Report(s)
-
The gold standard treatment for end-stage heart failure is heart transplantation; however, the rate of transplantation remains inadequate because of the paucity of organ donation. The left ventricular assist device (LVAD) has been used as a bridge therapy before transplantation. The LVAD is being used increasingly because it reduces mortality despite the accompanying morbidities. Therefore, the anesthetic management of LVAD-related morbidities is important and requires experience and knowledge. Herein, we describe a 60-year-old male patient with an LVAD with complaints of right hemiparesis, dysphasia, and facial paralysis. We aim to present the anesthetic management of a patient with intracranial hemorrhage who underwent LVAD exchange due to thrombosis.
-
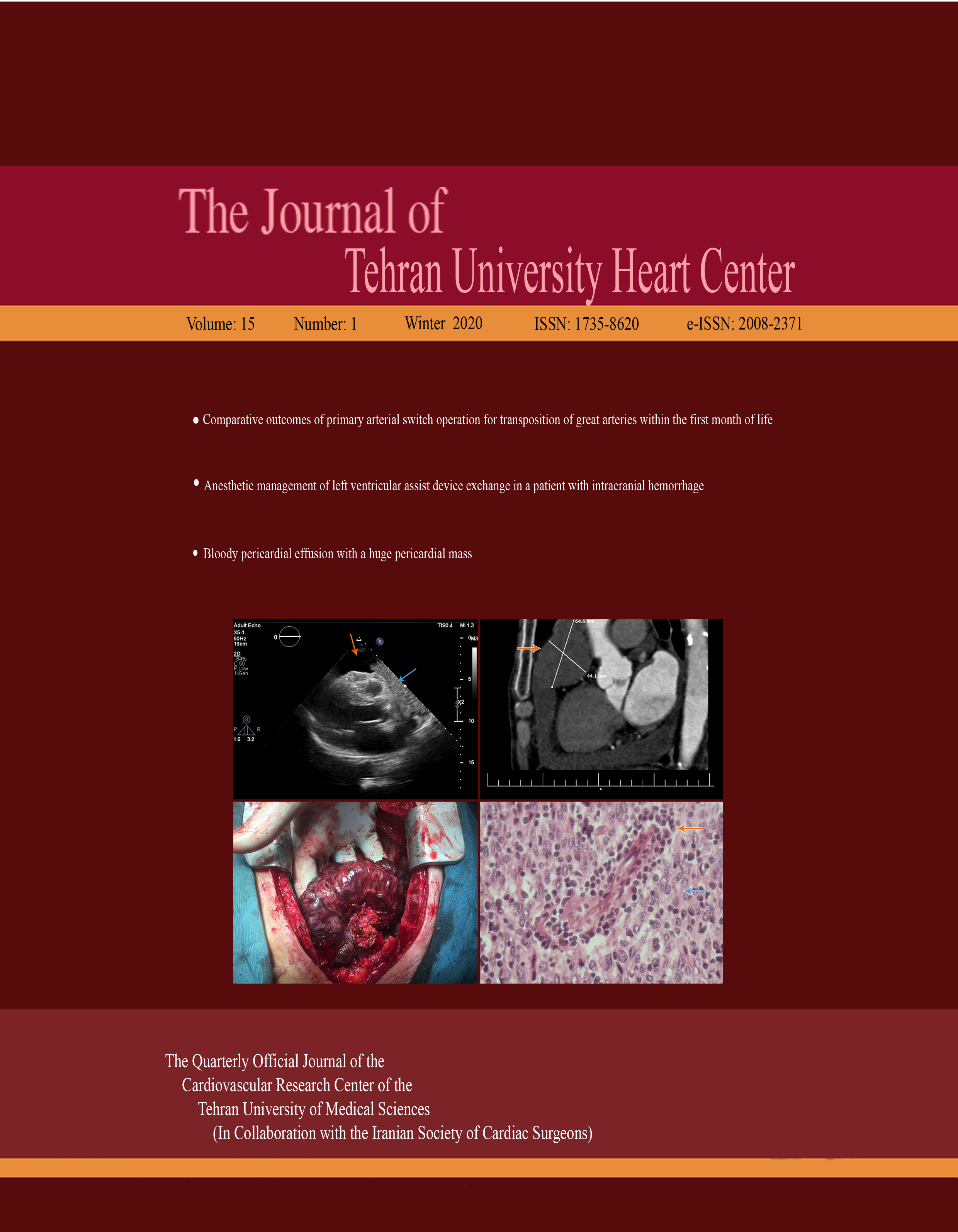
Nowadays, the early diagnosis of tumoral diseases is more possible and accurate with multiple diagnostic imaging modalities such as chest X-ray, echocardiography, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance imaging, especially for cardiac tumors which are usually asymptomatic, even in large sizes. In cardiac masses, the patients’ presentations are non- specific and dependent on the tumor size and site as well as its compressive effect on the adjacent structures. On the other hand, the first and last signs could be sudden cardiac death. However, cardiac masses are either benign or malignant and metastatic in their malignant type, and their definite diagnosis is only possible by surgical tumor resection and tissue biopsy. In this paper, we describe an old patient with severe pericardial effusion and an unusual intrapericardial tumor in transthoracic echocardiography, representing a rare case of a giant ectopic thymoma after surgical resection and pathologic assessment.
-
Congenitally corrected transposition of the great arteries (cc-TGA) is a rare congenital abnormality that occurs in 1 per 33000 live births. This abnormality comprises nearly 0.05% of all congenital heart defects, with at least 90% of cc-TGA patients having associated cardiac defects; some of these associated defects are, however, very rare. In this case report, we describe a 22-year-old man who referred to our hospital for the evaluation of hypertension and cardiac murmurs. Via echocardiography and catheterization, the patient was finally diagnosed with cc-TGA, bicuspid aortic valve, and coarctation of the aorta. He underwent successful percutaneous transarterial coarctoplasty without any complications at early and 6 months’ follow-up visits.
Letter to the Editor
-
--
-
None